Page 83 - Ekonomija i Biznis_May 2016.indd
P. 83
РУWБOРИRLКАD
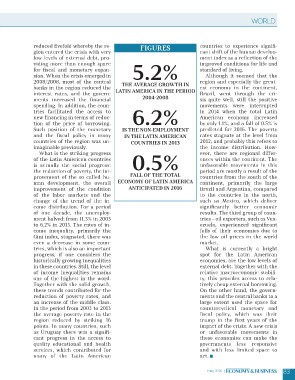
reduced fivefold whereby the re- Figures countries to experience signifi-
gion entered the crisis with very cant shift of the human develop-
low levels of external debt, pro- 5.2% ment index as a reflection of the
viding more than enough space improved conditions for life and
for fiscal and monetary expan- the average growth IN standard of living.
sion. When the crisis emerged in LATIN AMERICA in the period
2008/2008, most of the central Although it seemed that the
banks in the region reduced the 2004-2008 region and especially the great-
interest rates, and the govern- est economy in the continent,
ments increased the financial 6.2% Brazil, went through the cri-
spending. In addition, the coun- sis quite well, still the positive
tries facilitated the access to IS THE NON-EMPLOYMENT movements were interrupted
new financing in terms of reduc- in the Latin American in 2014 when the total Latin
tion of the price of borrowing. American economy increased
Such position of the monetary countries in 2013 by only 1.1%, and a fall of 0.5% is
and the fiscal policy in many predicted for 2016. The poverty
countries of the region was un- 0.5% rates stagnate at the level from
imaginable previously. 2012, and probably this refers to
FALL OF the total the income distribution. How-
What is the striking progress economy of Latin America ever, there are regional differ-
of the Latin American countries ences within the continent. The
is actually the social progress: ANTICIPATED IN 2016 unfavorable movements in this
the reduction of poverty, the im- period are mostly a result of the
provement of the so called hu- countries from the south of the
man development, the overall continent, primarily the large
improvement of the condition Brazil and Argentina, compared
of the labor markets and the to the countries in the north,
change of the trend of the in- such as Mexico, which deliver
come distribution. For a period significantly better economic
of one decade, the unemploy- results. The third group of coun-
ment halved: from 11.3% in 2003 tries – oil exporters, such as Ven-
to 6.2% in 2013. The rates of in- ezuela, experienced significant
come inequality, primarily the falls of their economies due to
Gini index, stagnated, there was the low oil prices in the world
even a decrease in some coun- market.
tries, which is also an important
progress, if one considers the What is currently a bright
historically growing inequalities spot for the Latin American
in these countries. Still, the level economies, are the low levels of
of income inequalities remains external debt. Together with the
one of the highest in the word. relative macroeconomic stabili-
Together with the solid growth, ty, this provides access to rela-
these trends contributed for the tively cheap external borrowing.
reduction of poverty rates, and On the other hand, the govern-
an increase of the middle class. ments and the central banks to a
In the period from 2003 to 2013 large extent used the space for
the average poverty rate in the countercyclical monetary and
region reduced by striking 16 fiscal policy, which was their
points. In many countries, such trump in the first years of the
as Uruguay there was a signifi- impact of the crisis. A new crisis
cant progress in the access to or unfavorable movements in
quality educational and health these economies can make the
services, which contributed for governments less responsive
many of the Latin American and with less limited space to
act.
May 2016 83