Page 55 - E&B_septemvri 2015 ENG.indd
P. 55
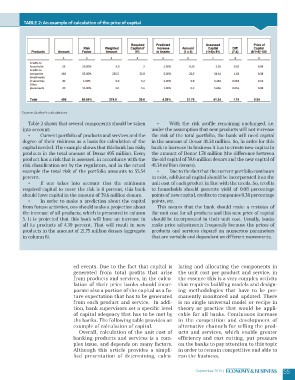
Table 2: An example of calculation of the price of capital RUBRIKA
Source: Author’s calculations
Table 2 shows that several components should be taken • With the risk profile remaining unchanged, i.e.
into account: under the assumption that new products will not increase
the risk of the total portfolio, the bank will need capital
• Current portfolio of products and services and the in the amount of Denar 41.34 million. So, in order for this
degree of their riskiness as a basis for calculation of the bank to increase its business it has to create new capital in
capital needed. The example shows that this bank has risky the amount of Denar 1.74 million (the difference between
products in the total amount of Denar 495 million. Every the old capital of 39.6 million denars and the new capital of
product has a risk that is assessed, in accordance with the 41.34 million denars).
risk classification set by the regulators, and in the actual
example the total risk of the portfolio amounts to 55.54 • Due to the fact that the current portfolio continues
percent. to exist, additional capital should be incorporated into the
unit cost of each product in line with the needs. So, credits
• If one takes into account that the minimum to households should generate yield of 0.08 percentage
required capital to cover the risk is 8 percent, this bank points of new capital, credits to companies 0.38 percentage
should have capital in the amount of 39.6 million denars. points, etc.
• In order to make a prediction about the capital This means that the bank should make a revision of
from future activities, one should make a projection about the unit cost for all products and this new price of capital
the increase of all products, which is presented in column should be incorporated in their unit cost. Usually, banks
5. It is projected that this bank will have an increase in make price adjustments frequently because the prices of
all its products of 4.39 percent. That will result in new products and services depend on numerous parameters
products in the amount of 21.75 million denars (aggregate that are variable and dependent on different movements.
in column 6).
ed events. Due to the fact that capital is lating and allocating the components in
generated from total profits that arise the unit cost per product and service, in
from products and services, in the calcu- the essence this is a very complex activity
lation of their price banks should incor- that requires building models and design-
porate also a portion of the capital as a fu- ing methodologies that have to be per-
ture expectation that has to be generated manently monitored and updated. There
from each product and service. In addi- is no single universal model or recipe in
tion, bank supervisors set a specific level theory or practice that would be appli-
of capital adequacy that has to be met by cable for all banks. Continuous increase
the banks. The following table provides an in the competition and development of
example of calculation of capital. alternative channels for selling the prod-
ucts and services, which enable greater
Overall, calculation of the unit cost of efficiency and cost cutting, put pressure
banking products and services is a com- on the banks to pay attention to this topic
plex issue, and depends on many factors. in order to remain competitive and able to
Although this article provides a simpli- run the business.
fied presentation of determining, calcu-
September 2015 55